Alimentary Canal and Digestive Glands
Alimentary Canal and Digestive Glands: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Digestive System, Gall Bladder, Pancreas, Stomach, Teeth, Tongue, Anus, Rectum, Mouth, Colon, Small Intestine, Salivary Glands, Large Intestine, Parotid Gland, Epiglottis, Duodenum, Oesophagus and, Alimentary Canal
Important Questions on Alimentary Canal and Digestive Glands
Functional units of food absorption are:
Damage to which gland of the buccal cavity would lead to an increase in the concentration of triglycerides in the esophagus?
The pathway with which Bile salts move-
One of the constituents of the pancreatic juice which is poured into the duodenum in humans, is:
Pancreatic juice and hormones of pancreas are produced by:
If for some reason our goblet cells are non functional, this will adversely affect:
Which one of the following is the correct matching of the site of action on the given substrate, the enzyme acting upon it and the end product ?
What will happen if the secretion of parietal cells of gastric glands is blocked with as inhibitor?
In man, the zymogen or chief cells are mainly found in:
Parotid salivary glands occur:
Epithelial cells of the intestine involved in food absorption have _________ on their surface.
Duodenum has characteristic Brunner’s gland, which secretes two hormones called:
The contraction of gall bladder is due to
The layer of cells that secrete enamel of tooth is:
Wharton’s duct is associated with:
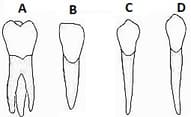
Identify teeth labelled as A–D in the given figure.
Most of the fat digestion occurs in:
Brunner’s glands occur in:
Duct leading from parotid gland and opening into vestibule is:
Which of the following functions is not performed by secretions from salivary glands?
